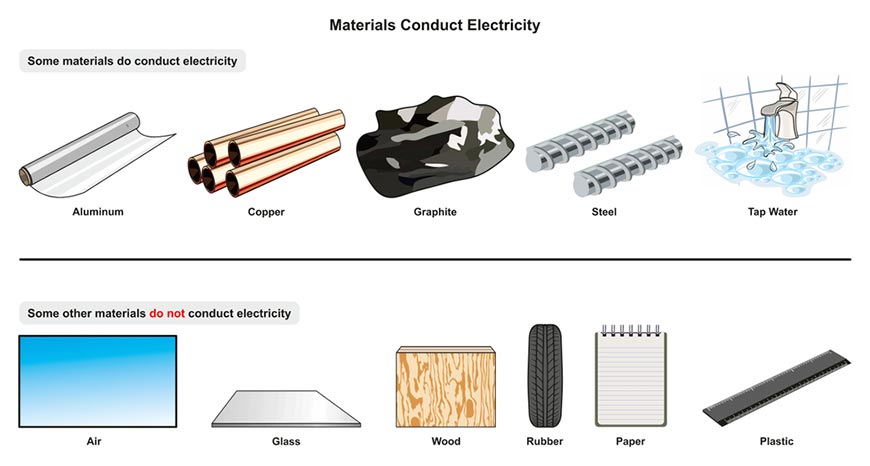
Safety rules in chemistry labs
What is Safety in the laboratory? What are the general regulations at the laboratory along with the rules of the laboratory? What are the responsibilities of officers and employees? When working in the laboratory and working directly with chemicals, what should you pay attention to to ensure your safety? Finally, how is first aid for injuries and poisoning cases in the laboratory? All will be in the article below of Hiep Phat.
What is Lab Safety?

Laboratory safety is the criteria set forth for those who work in the laboratory to adhere to. Obeying and complying with these regulations and rules will help laboratory research processes be performed more safely and effectively, avoiding unnecessary risks.
In any field of magnetism, biology, physics or medicine,… laboratory safety is paramount.
To ensure safety, avoid unfortunate situations when working in the Laboratory, each officer and employee working at The laboratory must master the procedures, regulations and strict compliance. Along with that, it is extremely necessary to equip and use labor protection equipment.
General laboratory safety regulations
The following are general laboratory rules to ensure safety during work and research. That is:
- Always be aware of where to put safety equipment.
- Must wear a lab coat.
- Goggles must be worn.
- You must tie your hair up.
- Experiments can only be performed in the presence of the teacher or the person in charge of the laboratory.</ li>
- Read the instructions carefully and think before doing the experiment.
- Clean the lab table before starting an experiment.
- Never taste lab chemicals. Do not eat or drink in the laboratory.
- Do not look down the test tube.
- If chemical gets into eyes, wash eyes immediately.
- Dispose of laboratory waste in the correct place as directed.
- If you’re unsure, ask.
- If chemical spill or accident occurs, notify teacher immediately.
- Wash skin when in contact with chemicals.
Notes for officials and employees working in the laboratory

To ensure safety, when entering the laboratory we need:
- Clean the lab table before conducting the experiment
- Do not swallow, do not drink laboratory chemicals
- Wash skin after contact with chemicals
- Read instructions for using chemicals carefully and think carefully before doing experiments
- Wear goggles, gloves, medical mask and lab gown
- If you accidentally get chemicals in your eyes, you need to wash them immediately
- Dispose of laboratory waste in the correct place as directed
- Tie your hair neatly, avoid exposure to harmful chemicals
Everyone working in the laboratory must learn and be tested on occupational safety regulations, master procedures, technical regulations and measures to ensure occupational safety.
Must read the document carefully, understand all the details of the experiment before doing it, and anticipate possible problems to proactively prevent avoid.
In conducting the experiment, it is necessary to observe and carefully record the data to make a test report. After work, must clean and neatly arrange laboratory equipment and tools.
Replace chemicals and laboratory equipment where they are. Before leaving the laboratory, it is necessary to check the laboratory again, close the water valves, close the circuit breaker, …
Regulations for lab staff

- Hair must be neat, if long hair must be tied neatly, Nails must be neatly cut, no jewelry when working.
- Use personal protective equipment in accordance with regulations on occupational safety.
- The employees of the Chemistry Department strictly follow the factory’s occupational safety regulations.
- No smoking in the Laboratory.
- Do not use contact lenses while working in the Laboratory.
- No eating in the lab.
Laboratory safety regulations

- Carefully check laboratory equipment and instruments before use.
- When distilling water, it is necessary to regularly check the water source to the device to prevent dehydration.
- When finished using equipment such as furnaces, ovens, stoves…in the laboratory, the equipment switches must be turned off and turn off the power.
- The chemistry laboratory must be equipped with exhaust fans and emergency showers.
- Do not pour raw chemicals into appliance sinks or drains as this is dangerous.
- Do not look at chemicals or boiling liquids to avoid splashing into eyes.
- Must know the necessary positions to be able to operate quickly and safely.
- After the experiment is done, wash the cleaning tools to the right place and keep the workplace clean, dry.
- Clean the workbench and workshop after each shift.
- Wear gloves when collecting broken glass.
- Do not leave items, chemicals on the floor, on the aisle.
- All incidents in the Laboratory are fully recorded in the incident log, and immediately reported to the Chief ca Head of Quality Management Department or PAT.
- Before leaving, check the equipment and turn off the power.
Laboratory chemical control regulations

- Unused laboratory chemicals must be stored in a separate cabinet.
- Chemicals in the cabinet must be stored separately and in a separate area for identification.
- A log book must be kept to monitor incoming and outgoing chemicals. Periodic inspection of stored chemicals.
- Regularly check chemical packaging to avoid damage, leakage, and spillage. If the chemical tank is spilled or broken, collect the chemicals immediately, arrange for immediate use or change the packaging, and clean the remaining chemicals properly.
- Label each chemical vial. The label must record the condition of the chemical bottle: date of receipt, date of opening of bottle, date of expiry date…
- Toxic chemicals must be strictly managed in the allocation: quantity, purpose of use, recipient. The person who authorizes the distribution of toxic chemicals is the Head of Quality Control Department.
- The chemical laboratory must have a list of toxic chemicals. The catalog is updated regularly.
Safety regulations when transferring laboratory chemicals
- All chemical bottles and cups must be clearly labeled.
- Check the chemical label on the bottle before pouring.
- Always fill the burette under the eye. For hazardous chemicals must be filled in a fume hood.
- When handling or moving chemicals, you must wear a respirator, gloves, and glasses.
- When filling, make sure not to spill or release dust.
Laboratory waste control
- Laboratory waste is controlled according to the Factory’s waste management regulations.
- Remaining raw sample solution must be collected at the sample supplier and returned to the sample delivery unit.< /li>
- The solution after testing the sample is collected to the wastewater treatment pond.
- Expired chemicals, spilled chemicals, waste packaging… that need to be disposed of must be placed in a suitable container , with a tight-fitting lid, labeled with the full name, not abbreviated. Notify regulatory authorities so that they can be disposed of properly.
Chemical safety regulations in the laboratory
Chemical safety is fundamental to the laboratory. In addition to safe and non-toxic chemicals, there are also extremely toxic substances that, if exposed, will easily cause skin corrosion, skin burns, blindness if falling into the eyes and more dangerous can cause fire and explosion. Therefore, when handling these chemicals must be extremely careful. Specifically:
Experiment with hazardous chemicals
HCN, Hg, CO, Cl2, NO, NO2, H2S, HgCl2, CH3OH, Benzene, Toluene, HCHO, CH2Cl2,… These are the chemicals The substance is found in a laboratory and is considered very toxic. When conducting experiments with this chemical, you need to keep a few points in mind:
Do not taste and swallow hazardous substances by mouth, be cautious when smelling hazardous substances. Do not smell chemicals directly, but only use your hands to gently blow chemical vapors into your nose.
For mercury should be stored in thick, tightly sealed jars and should be covered with a thin layer of water.
Limit, avoid inhaling bromine, chlorine and nitrogen gas, avoid getting into eyes or hands.
Clean hands and tools thoroughly with soap or other suitable substance after the experiment is complete.
Experiment with corrosive substances

Concentrated acids, concentrated alkalis, alkali metals, white phosphorus, phenols, etc. are corrosive substances that can be mentioned in the laboratory. When using these substances we should note:
The first thing when coming into contact with this chemical is to wear protective gloves, keep it away from people, clothes.< /span>
Should use goggles to avoid chemical splash in eyes.
Do not store concentrated acid in a container that is too large, when pouring, do not raise the bottle too high above the table.
When diluting sulfuric acid, it is necessary to pour acid into water, not vice versa.
When heating corrosive solutions, strictly follow the rules of heating chemicals in a test tube (point the mouth of the test tube towards the end of the tube). direction of no people).
Experiment with flammable and explosive substances

Heating or distilling is only allowed in a water bath or air-proof on a closed electric stove.
Do not store near heat sources, circuit breakers and other flammable substances
When working with explosive substances such as H2, lye, alkali metals, concentrated acids, flammable organic substances, … we need to wear protective glasses (made of organic glass) to protect the eyes and other important parts of the face
When heating solutions in a test tube, use a pair and always point the mouth of the test tube toward no one, especially when heating concentrated acids or alkaline .
What to do when an injury or poisoning occurs?
In case of burns
burns caused by flammable solvents such as benzene, acetone (C6H6, CH3COCH3, ….): Cover the burned area with a cloth or towel soaked in water on the victim, then use sand or wet sacks to put out the fire. Do not use water to wash the burn, but use gauze soaked in potassium permanganate (KMnO4 1%) or picric acid H3BO3 2% to gently place on the burn wound.
Burns caused by concentrated alkali: caustic soda, caustic potate (NaOH, KOH): Use clean water to wash the wound several times, then wash with 5% acetic acid solution. If alkali splashes into eyes, rinse with clean water several times after boric acid solution (H3BO3 2%).
Burns caused by concentrated acids such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid (H2SO4, HNO3…): First wash with clean water several times, then use a solution 5% ammonia or 10% NaHCO3 solution, remove acidic media on the burned area (soap should not be used to wash the wound). If acid gets into eyes, quickly rinse thoroughly several times with clean water, distilled water, cooled boiled water, then use 3% sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) solution.
For phosphorus burns: First wash the burn with 2% copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution. Do not use ointment. Next, use gauze impregnated with 2% copper sulphate solution or 3% potassium permanganate solution (KMnO4) to place on the wound. Burns of this type take longer to heal than other burns, need to avoid causing infection.
In case of poisoning
Poisoning by drinking acid by mistake: First give the victim ice water, crushed eggshell (1/2 teaspoon in a glass of water) and give magnesium oxide (MgO) powder mixed with water for drinking (29 grams in 300 grams). ml of water) and drink it slowly.
Poisoning by inhalation of alkalis (ammonia, caustic soda…): Give first aid to the victim by drinking diluted vinegar (2% acetic acid) or lemonade.
Poisoning by ingesting mercury compounds: First, make the victim vomit and then give milk mixed with egg whites. Then give the victim activated charcoal.
White phosphorus poisoning: First make the victim vomit, and then drink 0.5 g copper sulphate (CuSO4) solution in a liter of water and give ice water to drink. Do not drink milk, egg whites, grease because these substances dissolve phosphorus.
Lead poisoning: Give the victim 10% sodium sulphate (Na2SO4) or 10% magnesium sulphate (MgSO4) 10% in warm water because the This substance will form a precipitate with lead. Then drink egg white milk and drink activated charcoal.
Poisoning by inhaling toxic gases such as chlorine, bromine..(Cl2, Br2) need to take the victim to a fresh place, loosen the belt , breathe air with a small amount of ammonia or you can use a mixture of 900C alcohol with ammonia.
Poisoning due to inhalation of hydrogen sulfide, carbon oxide… The victim should be placed in a well-ventilated area, given pure oxygen, and performed artificial respiration if necessary.
Poisoning by inhalation of too much ammonia: Inhale hot steam, then give lemon juice or diluted vinegar.
Hopefully through the article you can better understand the concept lab safety as well as effective lab safety practices.

Leave your questions, we will answer them right away



 EN
EN VN
VN