What is a colony? Method of counting colonies on a petri dishes
What is a Colony How to count colonies on petri dishes quickly and accurately is the content that Hiep Phat will share in the article below.
What is a colony?

What is a colony? Colony of a type of cluster, or colony of bacteria, visible to the naked eye, the biomass of that bacterium as they grow on the surface of a shelf hard body. In the case of colonies growing from a single stem cell, their genomes are identical, and they are called a clone.
In simple terms, when we culture a certain type of bacteria in a favorable environment, they will grow and develop into a “collection” of bacteria visible to the eye, the “colony.”
We classify colonies based on: Culture medium, color and shape…
Unit
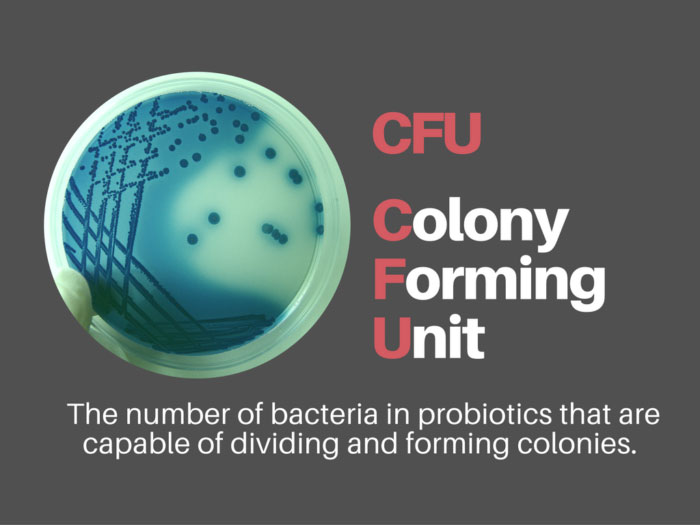
CFU
CFU (abbreviated from Colony form units) is a colony-forming unit, used to estimate the number of bacteria or fungal cells in a given test sample.
When examining for microorganisms in a test sample by counting colonies on a petri dish or prepared media dish (e.g. plate Compact Dry), units are usually CFU/mL, CFU/g, CFU/25g.
CFU/g , CFU/25g units are commonly used for solid test samples (food, food ingredients…)
CFU/mL unit for test samples in liquid form such as samples of aquaculture water, juice…
MPN
MPN (short for Most Probable Number), commonly used to indicate the number of bacteria present in a given volume of a liquid sample.
Difference between CFU and MPN
CFU is the colony-forming unit present in a given test sample. CFU is usually calculated from pour plate or inoculation method while MPN is usually calculated by fermentation method.
For CFU, bacteria grow on solid media (eg agar). The colonies were then counted manually by eye or by modern application.
Meanwhile with MPN measurement, samples are cultured in liquid medium, (e.g. fermentation). The result does not use the counting method, but compares it with the probability table.
MPN and CFU are equivalent. Both are recognized by many regulatory and scientific organizations around the world, including the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Colony Count Method
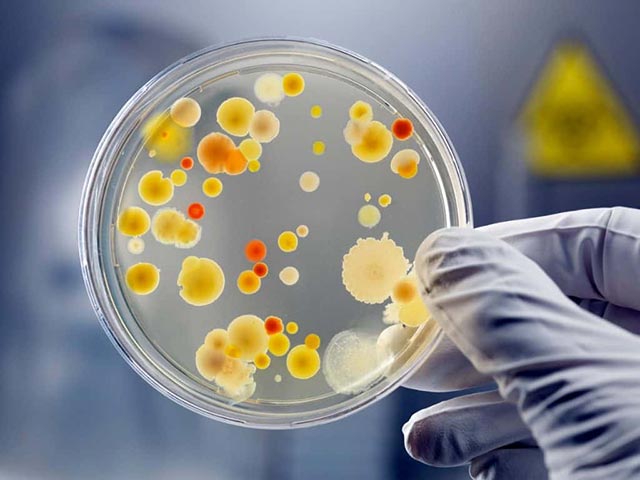
One of the classic ways to determine the density of microorganisms in a sample is to dilute the sample, inoculate the agar plate, and then count the microorganisms. colonies grow on it. Bacteria inoculated on growth plates form colonies from one or more of the original bacteria. These colonies can be seen and counted with the naked eye or a microscope. Colony counts are used to identify and count bacteria in soil, water, and food samples.
Sample dilution, inoculation and incubation
If you just create a simple microbial streak on the agar plate, there will be so many separate colonies that overlap each other making it impossible count the number of colonies. To solve this problem, mix the sample with the solution, taking a small amount of this initial sample suspension to further dilute it. Repeat this process 6 to 10 times. Brush the final diluent evenly onto the agar plate and incubate it for four to seven days before counting the colonies growing on it.
Manual colony counting method
The method of colony counting is to count each colony dot once. One approach is to place the petri dish on a grid of cells and count the colonies in each plot. It is also helpful to mark countable colonies on the back of a petri dish. In general, you will need to count at least three plates; only when using dishes containing 30 to 300 colonies to help draw reliable conclusions. Plates with too many or too few colonies are not suitable and need to be diluted and re-inoculated.
Automated colony counting method
Manual colony counting takes a lot of time and can be confusing due to subjective error of the operator. To improve this, automatic colony-counting devices can be used. City counter takes an image of the plate, separates the colonies from the background, and then uses an algorithm to Count the colonies on the plate. Algorithms can have difficulty distinguishing colonies when two or more colonies overlap at the edge, so this is an area of current software development.
Current popular colony counters
Funker Gerber Colony Star Colony Counter
- The work surface is 145 mm in diameter
- Automatic counter, count display
- Allows counting light and dark areas
- Compact, easy to clean
IUL SphereFlash Automatic Colony Counter
- Automatic colony capture and counting on 90 m Petri dishes
- Simple software, easy to use, control via computer, print report PDF file
- Audit Trail integrated software meets 21 CFR Part 11 standards (Colonies Pro software)
- Method can be adjusted to distinguish different types of colonies (Colonies Pro software)</ li>
- Built-in automatic counting programs
- Has “Auto Calibration & Validation”
- No reflection from the petri dish when shooting
- Can optionally add “Sterile measurement”
- Power supply: 90~264 V AC
- Size: 288x220x371 mm
- Weight: 5.5kg (12. 13 lb)
What are the limitations of the colony counting method?
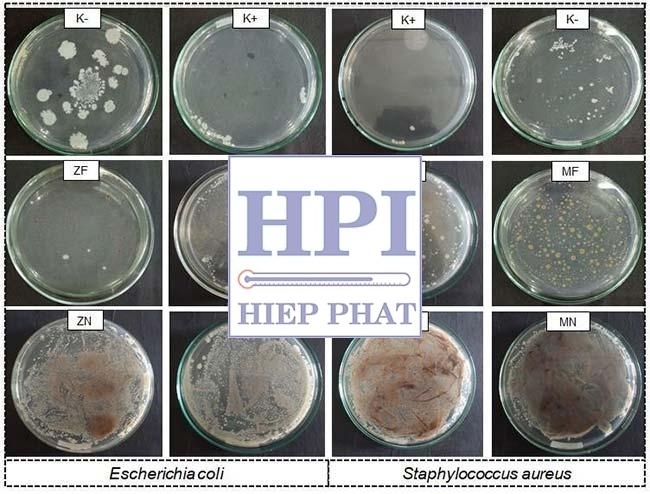
The accuracy of calculating bacterial densities from true colonies has some limitations. Colony-forming units can be a single cell, a series of cells, or a whole cluster of cells. Assuming that one colony represents one cell, then the calculated density may be low. Different bacteria need different growth conditions, and plate colonies represent only those bacteria that grow on culture media under those incubation conditions. Furthermore, this method does not account for dead cells, which needs to be considered carefully when you need the density of cells in the original sample.
The above article has provided some information about the concept of bacteria as well as current popular measurement methods. If you have any questions, or want to buy colony meters at Hiep Phat, do not hesitate to contact Hiep Phat via Hotline: (028) 6287 4765 or Email: sales@thietbihiepphat.com to receive timely advice.

Leave your questions, we will answer them right away



 EN
EN VN
VN